| J78/III/Qns
4
A sinusoidal
alternating p.d. is applied to a uniform metre wire AB as shown in Fig.
14.
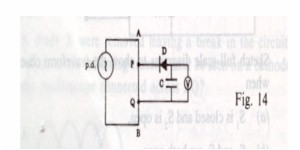
In this
circuit, C is a capacitance C, D is an ideal diode and V is a d.c.
voltmeter. The distance PQ is 30 cm. The voltmeter reads 2 V. Assuming
that the capacitance C and the resistance R of the voltmeter
are large,
(a)discuss
whether the voltmeter reads the r.m.s., the peak, or the mean value of
the p.d. across PQ,
(b)calculate
the r.m.s. value of the p.d. applied to the meter wire AB,
(c)explain
why the product RC must be large. |