|
|
SEMICONDUCTORS
An
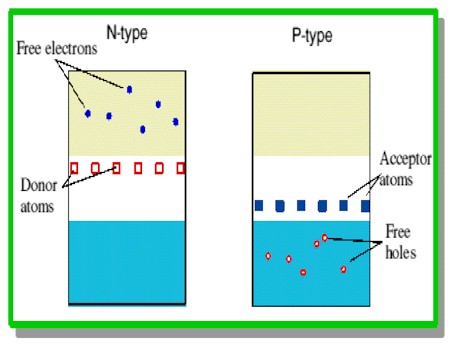
n-semiconductor is one whose conduction is mainly due to negative charges
or electrons, with positive charges (holes) as minority carriers.
A p-semiconductor
is one whose conduction is due mainly to positive charges or holes, with
negative charges (electrons) as minority carriers.
|
P-N
Junction Diode
A
diode is one which has an extremely high resistance in one direction but
a low resistance in the other. This allows current to flow in one direction
only.
Imagine
2 separate bits of semiconductors, one n-type, the other p-type.
 Symbol:
Symbol: |
Join
them together to make one piece of semiconductor which is doped differently
on either side of the junction.
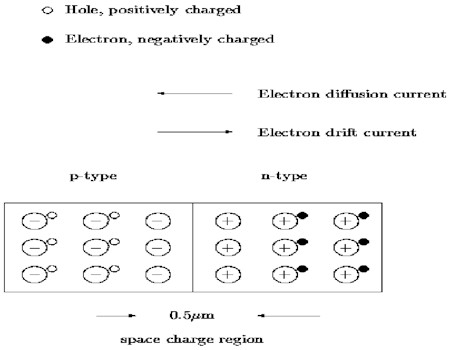
Free
electrons on the n-side and free holes on the p-side can initially wonder
across the junction. When a free electron meets a free hole it can “drop
into it”. This means the hole and electron cancel each other and vanish.
|
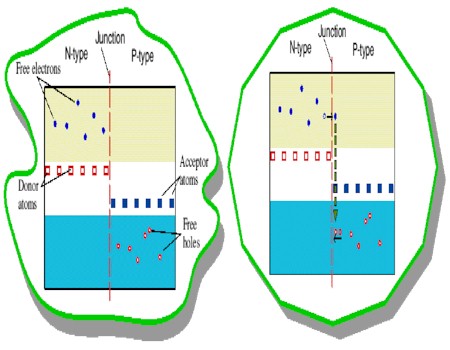
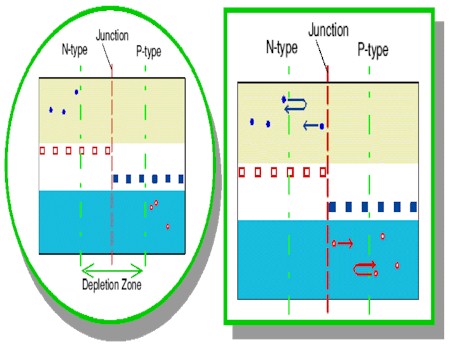 As
a result, the holes near the junction tend to 'eat' the free electrons
near the junction, producing a region depleted of any moving charges. This
creates what is called the depletion zone. Any free charge that enters
the depletion zone will find itself in a region with no other free charges.
Positive charges on the p-type side and negative charges on the n-type
side exert a force on the free charge, causing it to be driven back to
its 'own side' away from the depletion zone.
As
a result, the holes near the junction tend to 'eat' the free electrons
near the junction, producing a region depleted of any moving charges. This
creates what is called the depletion zone. Any free charge that enters
the depletion zone will find itself in a region with no other free charges.
Positive charges on the p-type side and negative charges on the n-type
side exert a force on the free charge, causing it to be driven back to
its 'own side' away from the depletion zone.
|
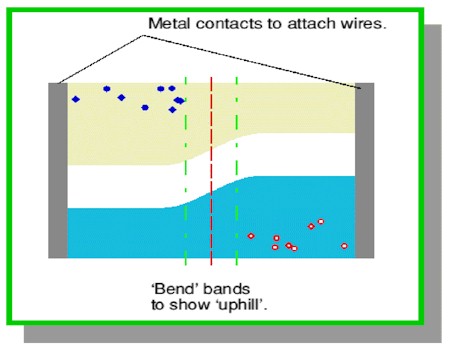 The
positive and negative charges are localised in the solid. The negative
charge of the acceptor’s extra electron and the positive charge of the
donor’s extra proton (exposed by the missing electron) tend to keep the
depletion zone clean of free charges once the zone is formed. A free charge
requires extra energy to overcome the forces from the donor/acceptor atoms
to be able to cross the zone. The junction therefore acts like a barrier,
blocking any charge flow across the barrier. In the diagram, electrons
are unable to flow from left to right as they are unable to move 'uphill'.
However, it is still possible for electrons to move to the right, ie downhill.
The
positive and negative charges are localised in the solid. The negative
charge of the acceptor’s extra electron and the positive charge of the
donor’s extra proton (exposed by the missing electron) tend to keep the
depletion zone clean of free charges once the zone is formed. A free charge
requires extra energy to overcome the forces from the donor/acceptor atoms
to be able to cross the zone. The junction therefore acts like a barrier,
blocking any charge flow across the barrier. In the diagram, electrons
are unable to flow from left to right as they are unable to move 'uphill'.
However, it is still possible for electrons to move to the right, ie downhill.
|
Types
Of P-N Junction Diodes
-
Glass enclosed
type
Angular
chip type
Glass
enclosed type
Mould
type
|
|
Forward
bias:
When the
p-type side is connected to the positive terminal of the battery and the
n-type to the negative, the junction is then forward bias.
Reverse
Bias:
If a battery
is connected across a p-n junction with its positive terminal joined to
the n-type side and its negative terminal to the p-type side, it helps
the junction voltage and the junction is said to be reverse biased. |
Back  Continue Continue
|
|